The move follows a price-drop test run in Q4 and comes with the addition of a “quality assurance card” from GIA for some loose diamonds.
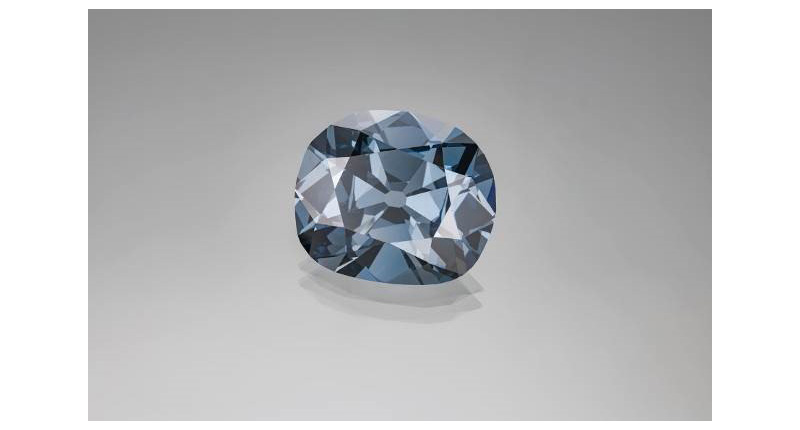
Going Deep: What the GIA Just Learned About Blue Diamonds
They don’t form in the same layer of the Earth as other diamonds.
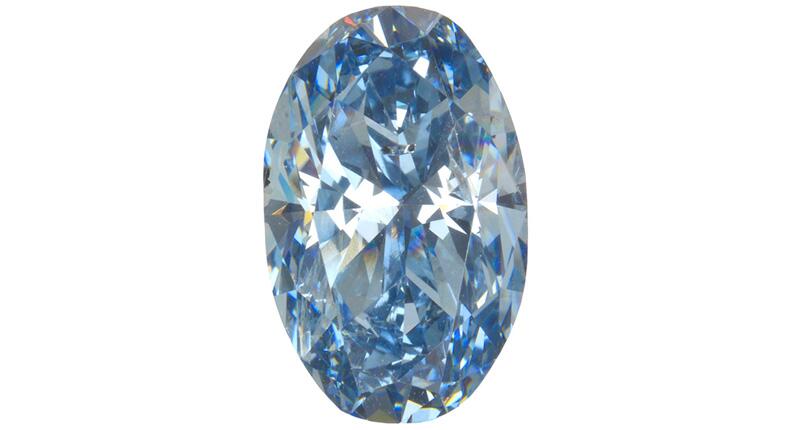

But scientists had no idea where exactly in the earth they formed or how they picked up the boron that makes them that color—until now.
Evan Smith, a research scientist at the Gemological Institute of America, was the lead author of an article that landed on the cover of the latest edition of the scientific journal Nature.
The article details the findings of a study he and other GIA researchers recently completed on inclusions in blue diamonds.
For this study, Smith examined 46 stones submitted to the GIA for grading over a two-year period.
“People”—meaning earth scientists, who look to diamonds to help draw hypotheses about Earth’s history—“have wanted to study these boron-bearing diamonds for years, but it’s difficult because they are rare and they’re also mostly inclusion-free,” he said.
“So if you do manage to borrow or purchase some of these blue diamonds, it’s difficult to learn much because they do not have inclusions.
(An article on blue diamonds in the Winter 1998 issue of Gems & Gemology authored by John King, et al states that in a study of more than 400 blue diamonds, researchers examined a subset of 62 stones specifically for inclusions. Of those, only about 15 had solid inclusions.)
Being at GIA, though, gave Smith access to a steady stream of boron-bearing diamonds with inclusions.
He said the graders would pick out stones that fit the profile and let him “borrow” them for a few hours. He would then use a non-destructive technique called Raman spectroscopy to identify what mineral was trapped inside the inclusions.
Over time, Smith assembled a list of inclusions that allowed him to draw conclusions about where and how blue diamonds form and to chart the movement of elements within the earth.
This is not the first time the researcher, whose work focuses on diamond geology, has been published outside of the jewelry industry.
Smith was the lead author of a study that appeared in Science magazine in January 2017 on the origins of diamonds of exceptional size and quality.
His most recent work dovetails nicely with his previous paper, as both involved studying diamonds to answer broader questions about the history of Earth.
Smith will present the findings from both studies at the upcoming GIA Symposium, which is scheduled to take place in October in Carlsbad.
For now, though, you can learn more about Smith’s revelations about the origins of blue diamonds in the interview below, which has been edited for length and clarity.
Evan Smith: This is a typical question because people often say, “They’re very rare; there are very few of them,” but it’s hard to find a number.
Very few people have been able to quantify it because to quantify this small number you really need to take a survey of millions of diamonds before you come up with a number that really means much of anything.
In the Nature article, I gave an estimate of 0.02 percent of mined diamonds being these Type IIb, these boron-bearing diamonds that are quite often blue. This is the best estimate we have for natural diamonds, so it is a very small proportion.
NJ: For sure. It’s rare to find these blues, and it’s even rarer to find them in large sizes, which is why we see bigger blue diamonds set records at auction.
ES: That’s precisely it. You could say something similar with the saturation of the color. Sometimes it’s very pale blue that’s barely noticeable but to have a large diamond that has a very pronounced blue color is exceedingly rare.

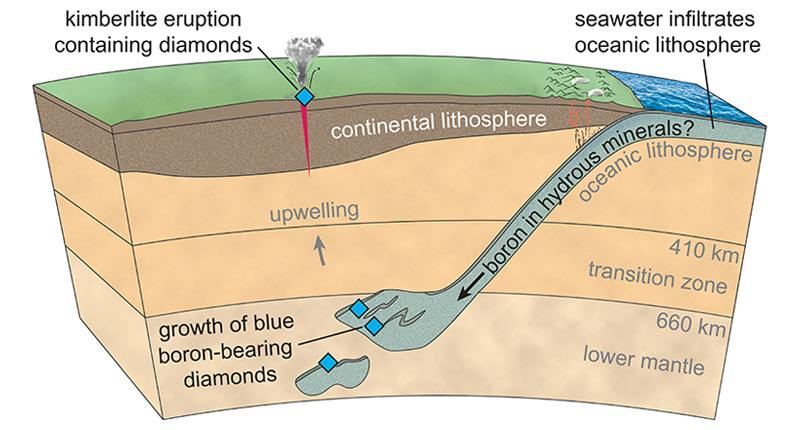
NJ: Let’s get into this study a bit. The article mentions that blue diamonds originate from depths reaching 410 miles. Are they forming deeper in the Earth than white, pink or yellow diamonds?
ES: This is a good question. The big finding from this study is the extreme depths at which they (blue diamonds) form. It’s maybe four times deeper than most other kinds of diamonds.
But it’s important to clarify that the blue color and the boron in these diamonds is not a direct result of depth. It’s not as if any time you form a diamonds very, very deep it’s going to be blue.
A better explanation would be that this is sort of a different recipe by which diamonds form; it’s like we are recognizing another process the Earth has to make diamonds, and we know there are multiple slightly different ways that diamonds can form.
We know, in general, that they come from very deep in the Earth, from the Earth’s mantle. Most gem diamonds form at a depth of between 150 and 200 kilometers (93 to 124 miles) in this part of the mantle that we call the continental plate.
Then there are some other kinds of diamonds that come from below that environment. The term that’s used to describe those diamonds is “superdeep,” or sublithospheric.
What we’ve recognized in this study is that these blue boron-bearing diamonds are actually part of this superdeep story—they form in a slightly different way and they form at really extreme depths.
Now the fact that they come from this extreme depth doesn’t immediately explain where the boron comes from; this is still a big question. But we have a really good hypothesis about that now.
One finding from this study was the extreme depth information. Another finding from this study was recognizing that the rocks surrounding the diamond when it was growing, sort of the host rock of this diamond birthplace, those rocks are oceanic rocks. They used to be at the earth’s surface; they used to be the oceanic tectonic plate.
Those rocks have sunken by the process of subduction; they’ve been dragged down deep into the Earth. And now these rocks that once were at the surface, making up the ocean floor, these rocks are now at a depth of 410 miles or deeper.
NJ: I always knew that blue diamonds were rare. I never knew that they actually formed deeper in the Earth than other natural colored diamonds.
ES: Nobody did. Prior to this study, there had been no single identification of any inclusion in a boron-bearing diamond, and we had no idea where they form or how they might be getting the boron that they contain.
NJ: When we are talking about the rocks surrounding the blue diamonds being the ancient ocean floor, how long ago are we talking? More than 500 million years?
ES: Most likely that’s what we are talking about.
We know that is certainly the case for blue diamonds that are from the Cullinan Mine in South Africa, for instance. A large portion of the blue diamonds in the market right now are coming from this mine.
We know the rocks at that mine are older than a billion years, so immediately it means the diamonds must have grown even farther back in time. So, in that case, the ancient ocean floor we are talking about is in excess of a billion years old.
NJ: The article also mentions the mineral inclusions in the blue diamonds you studied. Can you tell us more about these inclusions and how they helped form your hypotheses?
ES: These are minerals that are a little bit different from more common examples of mineral inclusions like olivine or garnet. These are minerals we don’t tend to see at the surface of the Earth; they’re not familiar.
The most common thing I was finding was a calcium silicate phase that would have once been in a very tightly packed crystal structure called perovskite. Calcium silicate perovskite is the most common thing we were finding.
There are a number of different silicate minerals that are exactly what you would expect to find if you took the sort of the ocean plate and increased the temperature and pressure to lower mantle conditions.
The minerals we were seeing are things we know only really exist deep in the Earth.

NJ: Why are these revelations about blue diamonds important?
ES: The reason why it’s in (the scientific journal) Nature is because it touches on a very big-picture type of question, and that is: How can the earth take material from the surface and transport them inside the Earth, sort of bring them into the earth’s interior?
The biggest question is surrounding water. We know that ocean rocks interact with the ocean, and it’s of great interest in Earth science to figure out if any of his ocean water, and other elements inside that environment at the surface, if any of that material can be transported to the earth’s interior.
It’s kind of surprising that blue diamonds have something to say about this question because immediately you don’t see any kind of connection. It’s kind of surprising that this big-picture story comes out of looking at blue diamonds.
NJ: Is there anything else from this study that’s important for readers to know?
ES: I would say there are three big findings from this study, and we didn’t really develop the third finding in full.
The first one is the depth information.
The second is that the rocks they (blue diamonds) are forming in look like they are oceanic rocks.
But the third thing, using that as an explanation for where this boron came from, is that the boron probably came from the ocean. Now that’s a hypothesis at this point, but it really seems like it’s the most likely explanation.
The boron started out in the ocean, and it was sort of chemically attached to the rocks on the ocean floor. Then these rocks were carried deep into the Earth and, in special circumstances, it looks like that boron can actually hitch a ride all the way down to the lower mantle.
This is the part that makes it interesting for the broader scientific community, showing that you’ve got a real pathway here to get boron and, by proxy water, from the surface down deep into the Earth.
It adds another layer of complexity. If you’re looking at the Hope Diamond, imagine that those little boron atoms that are giving it this color, that they might have actually been floating around the ocean at one point.
The Latest

The site has been down since Thursday evening, just ahead of its spring auctions.

The late former U.S. Secretary’s collection went for quadruple the sale’s pre-sale estimate.

Despite the rising prices, consumers continue to seek out the precious metal.

Three fifth graders’ winning designs were turned into custom jewelry pieces in time for Mother’s Day.


Kimberly Adams Russell is taking over the role from her father, David Adams, marking the third generation to hold the title.

As a token of womanhood, this necklace depicts when Venus was born from the sea.

Tradeshow risks are real. Get tips to protect yourself before, during and after and gain safety and security awareness for your business.

The deal gives the retailer control over the distribution of Roberto Coin jewelry in the U.S., Canada, Caribbean, and Central America.

Show your mother some love with a piece of fine jewelry.

The company’s Easton location will remain open.

Brian D. Fleming of Carla Corporation was elected to serve a one-year term in the role.


Sponsored by the Las Vegas Antique Jewelry and Watch Show

M.S. Rau is set to open a seasonal gallery in the high-end resort town early next month.

The branded jewelry market is thriving, said Richemont Chairman Johann Rupert.

The six designers, all participants in the show’s Diversity Action Council mentorship program, will exhibit in Salon 634.

The highlight of his collection is the coveted Patek Philippe Grandmaster Chime, which could sell for up to $5 million.

The “Venetian Link” series modernizes the classic Veneziana box chain in its bracelets and necklaces.

The Seymour & Evelyn Holtzman Bench Scholarship will provide tuition assistance to two low-income students.
The Swiss watchmaker said the company’s plans to use a new version of the Hallmark crown on jewelry would confuse consumers.

The executive talked about the importance of self-purchasers and how fuel cell electric vehicles are going to fuel demand for platinum.

The Indian jeweler’s new store in Naperville, Illinois marks its 350th location, part of its ongoing global expansion plans.

It will award a graduating high school student with about $10,000 toward a GIA diploma and an internship with the Seattle-based jeweler.

Wheat Ridge, Colorado police took a 50-year-old man into custody Wednesday following a two-month search.

PGI partnered with four new and seven returning designers for its annual platinum capsule collection.

Nicolosi, president and CEO of The Kingswood Company, previously sat on WJA’s board from 2011 to 2018.

Karina Brez’s race-ready piece is a sophisticated nod to the horse-rider relationship.




























